Module aws.redshiftdata
ballerinax/aws.redshiftdata Ballerina library
Overview
Amazon Redshift is a powerful and fully-managed data warehouse service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS), designed to efficiently analyze large datasets with high performance and scalability.
The ballerinax/aws.redshiftdata package allows developers to interact with Amazon Redshift Data API seamlessly using Ballerina. The Redshift Data API simplifies data access by eliminating the need for managing persistent database connections or the Redshift JDBC driver.
Setup guide
Login to AWS Console
Log into the AWS Management Console. If you don’t have an AWS account yet, you can create one by visiting the AWS sign-up page. Sign up is free, and you can explore many services under the Free Tier.
Create a user
-
In the AWS Management Console, search for IAM in the services search bar.
-
Click on IAM
-
Click Users
-
Click Create User
-
Provide a suitable name for the user and continue
-
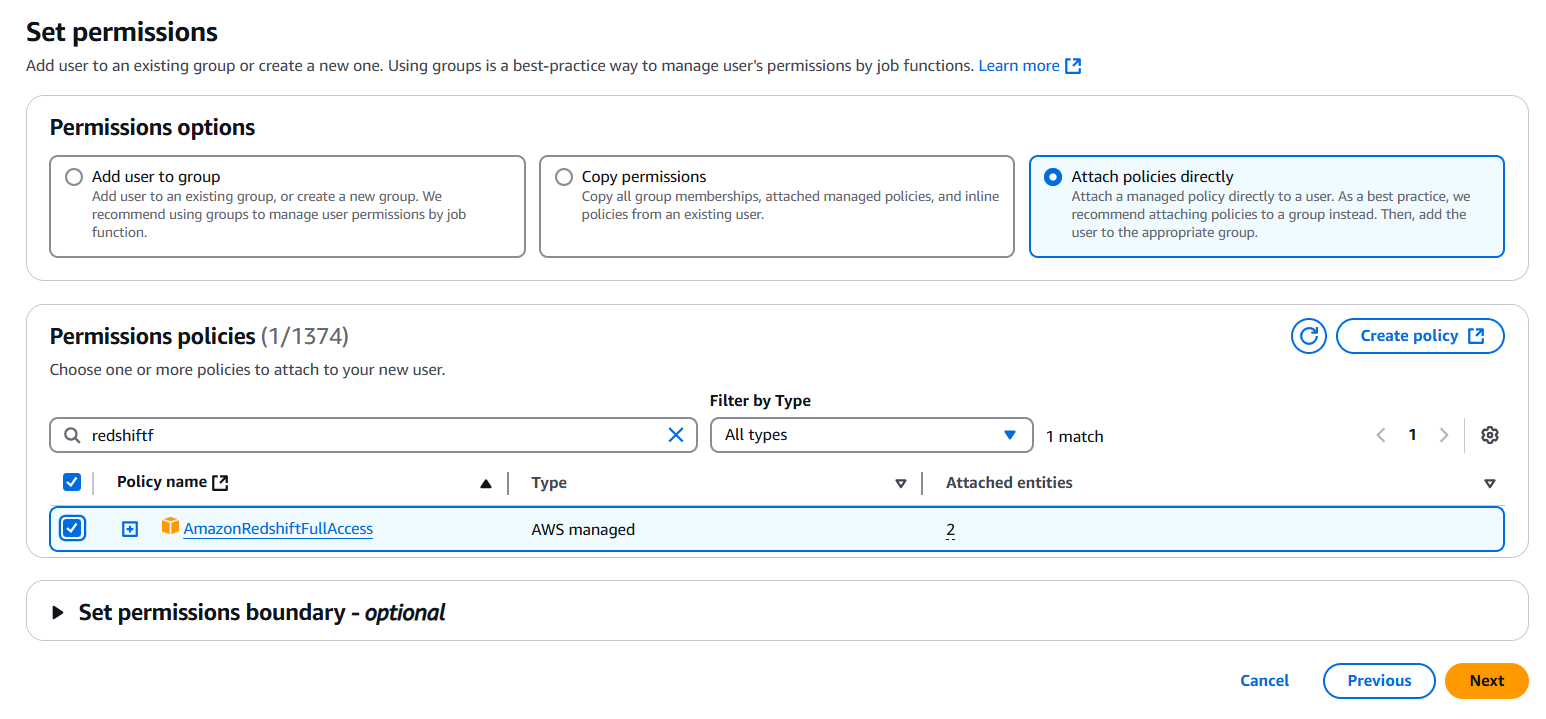
Add necessary permissions by adding the user to a user group, copy permissions or directly attach the policies. And click next.
-
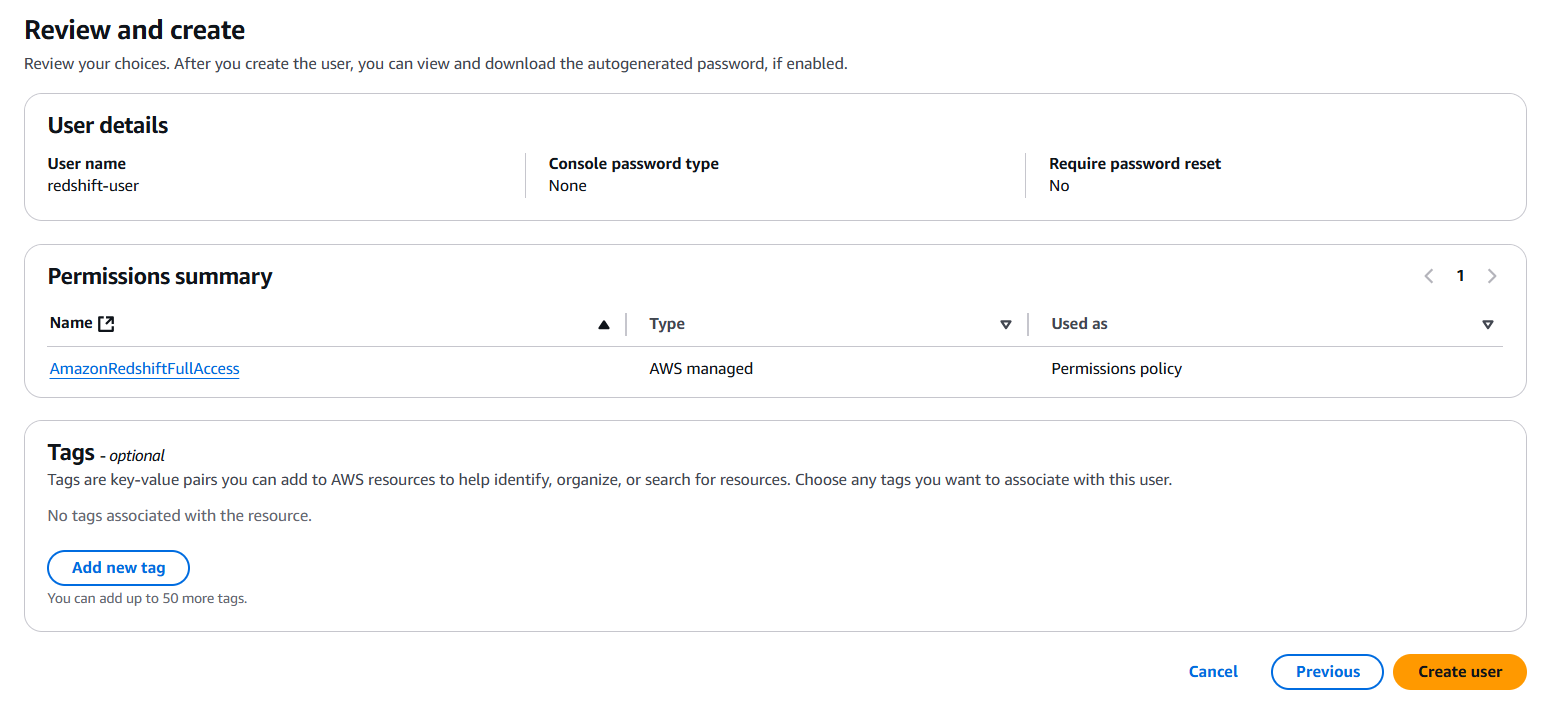
Review and create the user
Get user access keys
-
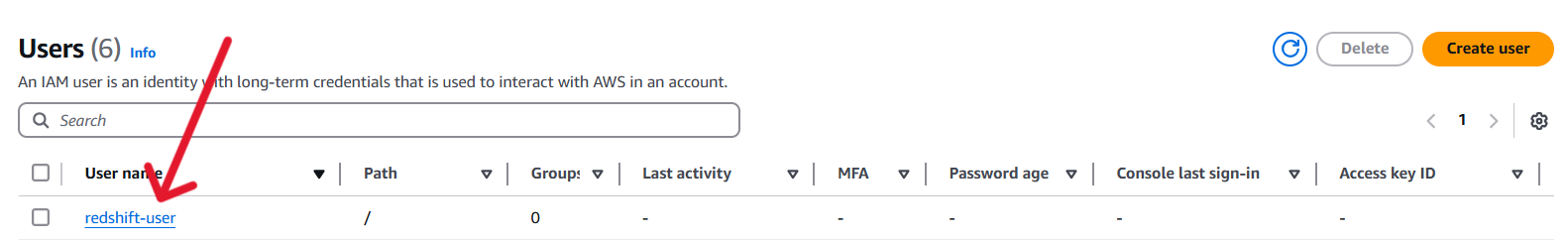
Click the user that created
-
Click
Create access key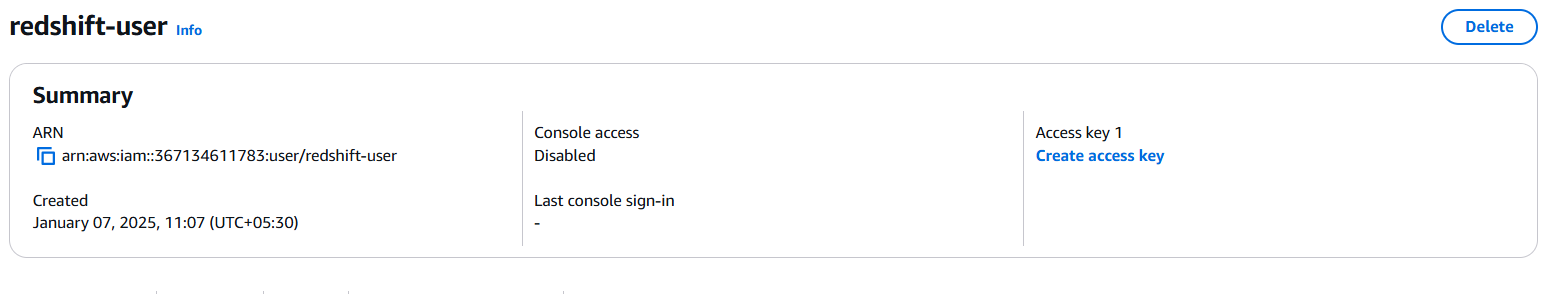
-
Click your use case and click next.
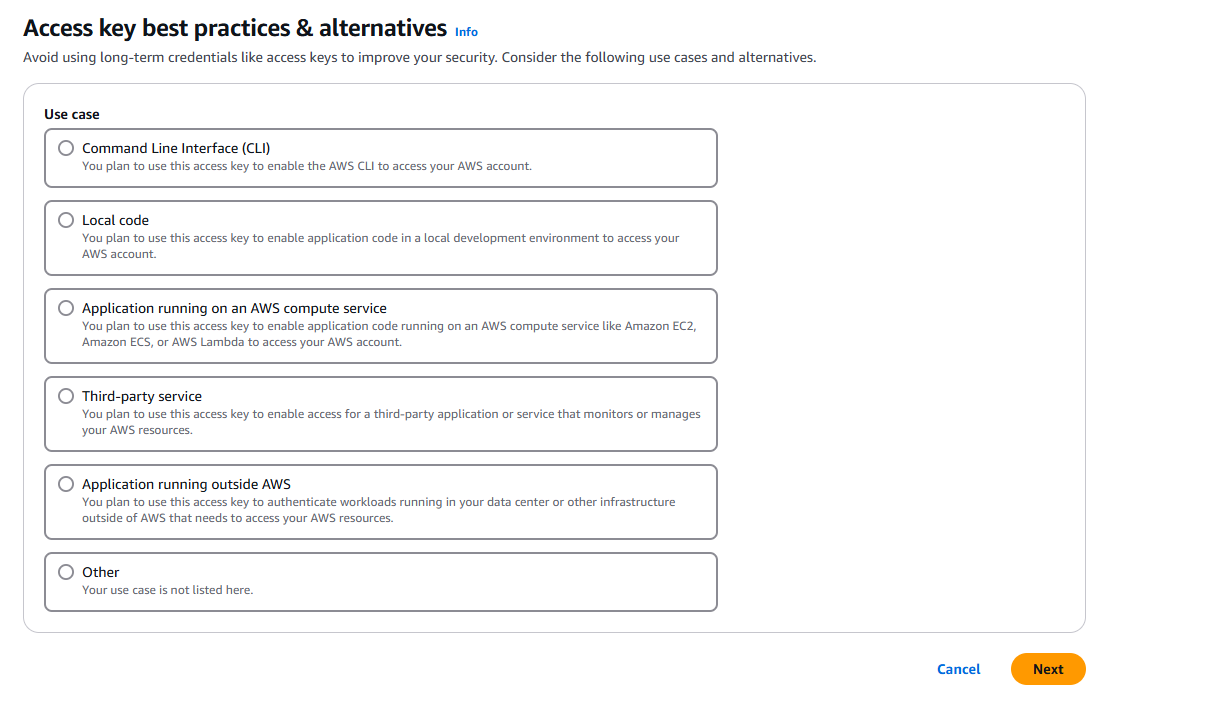
-
Record the Access Key and Secret access key. These credentials will be used to authenticate your Ballerina application with the Redshift cluster.
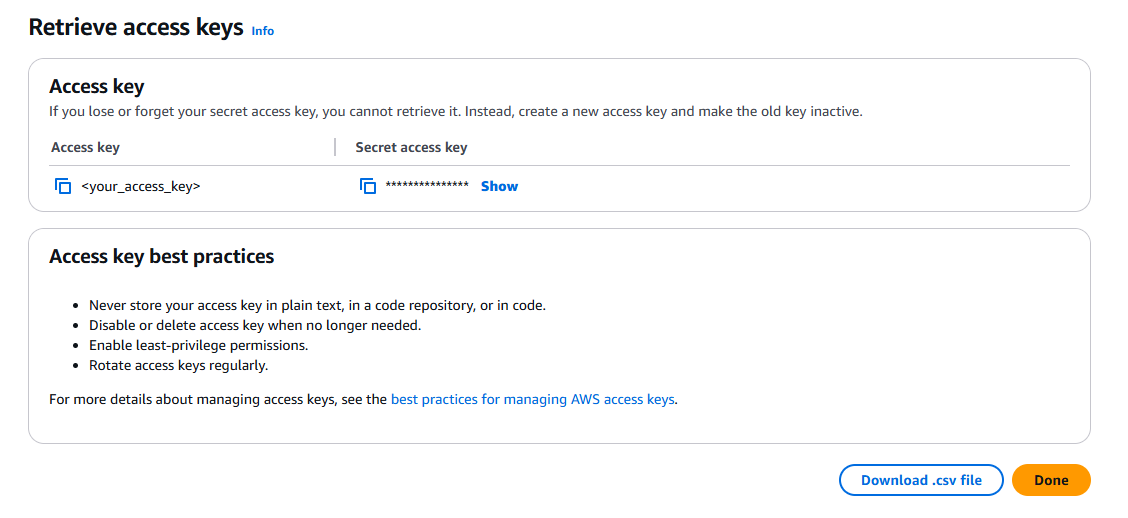
Setup a Cluster
To use the Ballerina AWS Redshift data connector, follow these steps to set up an Amazon Redshift cluster:
Step 1: Navigate to Amazon Redshift and create a cluster
-
In the AWS Management Console, search for Redshift in the services search bar.
-
Click on Amazon Redshift.
-
Click on the
Create clusterbutton to initiate the process of creating a new Amazon Redshift cluster.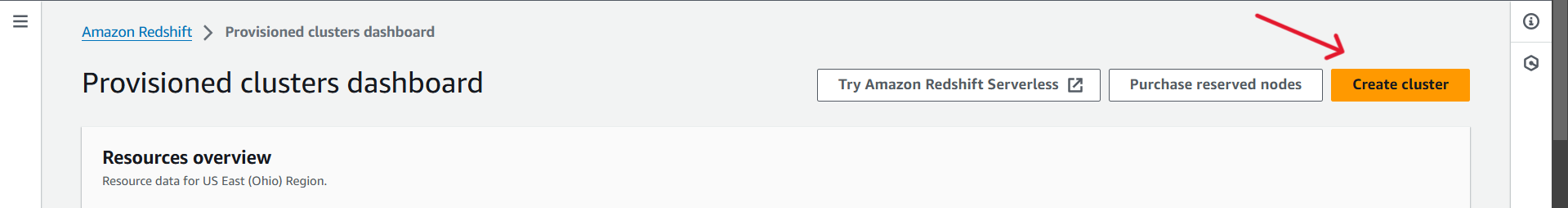
Step 2: Configure cluster settings
-
Configure your Redshift cluster settings, including cluster identifier, database name, credentials, and other relevant parameters.
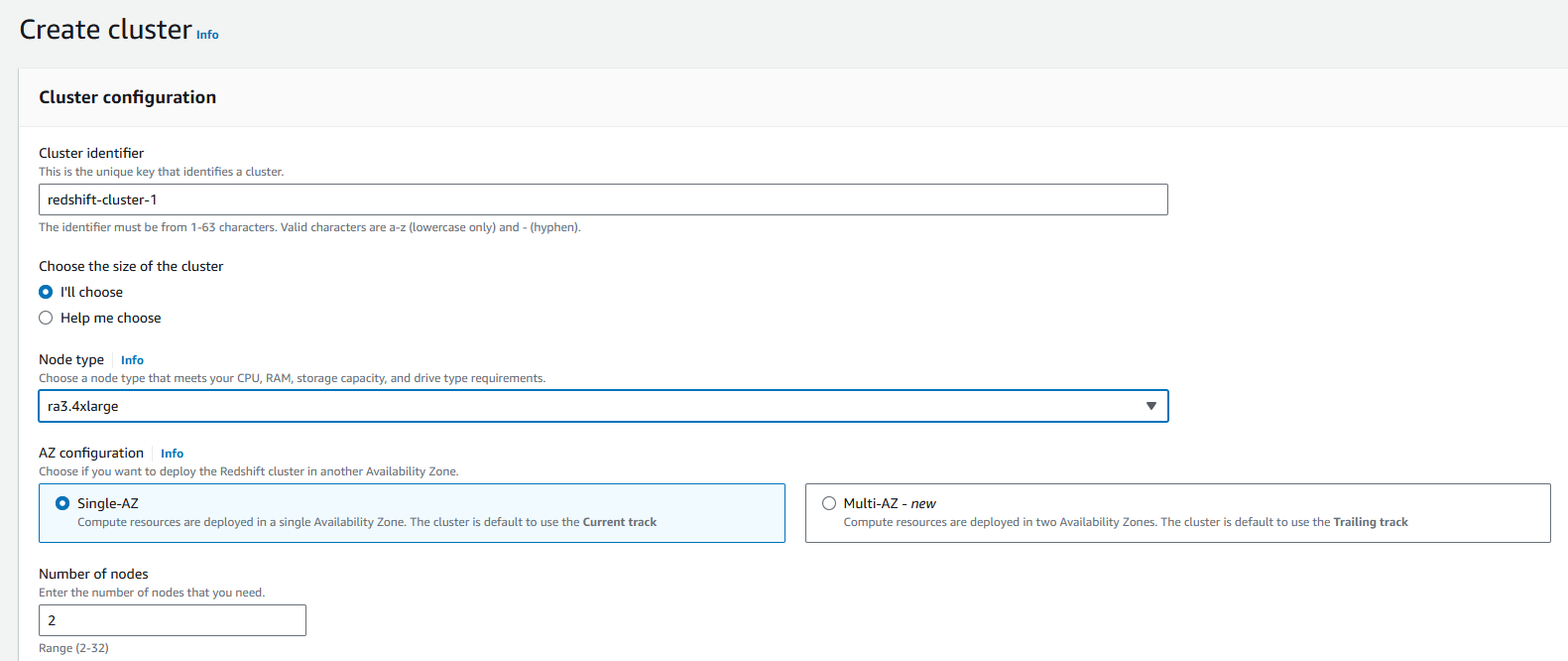
-
Configure security groups to control inbound and outbound traffic to your Redshift cluster. Ensure that your Ballerina application will have the necessary permissions to access the cluster.
-
Record the username during the cluster configuration. This will be used to authenticate your Ballerina application with the Redshift cluster.
-
Finally, review your configuration settings, and once satisfied, click
Create clusterto launch your Amazon Redshift cluster.
Step 3: Wait for cluster availability
-
It may take some time for your Redshift cluster to be available. Monitor the cluster status in the AWS Console until it shows as "Available".
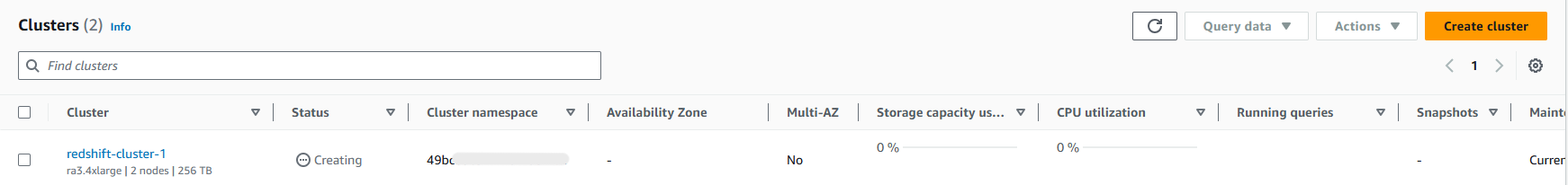
Note: Amazon Redshift now offers a serverless option, allowing you to use the data warehouse without managing infrastructure. Redshift Serverless automatically scales to handle your workloads, providing a flexible and efficient way to run analytics. To configure a Redshift serverless setup, please refer to AWS documentation.
Quickstart
To use the aws.redshiftdata connector in your Ballerina project, modify the .bal file as follows:
Step 1: Import the module
import ballerinax/aws.redshiftdata;
Step 2: Instantiate a new connector
Create a new redshiftdata:Client by providing the region, authentication configurations and dbAccessConfig.
The dbAccessConfig in the ConnectionConfig record defines the database access configuration for connecting to the Redshift Data API. It can be set to either a Cluster or a WorkGroup (Serverless mode). Additionally, users can override this configuration for specific requests by providing it in individual calls to methods like execute or batchExecute, allowing for more granular control over database access per execution.
configurable string accessKeyId = ?; configurable string secretAccessKey = ?; configurable redshiftdata:Cluster dbAccessConfig = ?; redshiftdata:Client redshiftdata = check new ({ region: redshiftdata:US_EAST_2, auth: { accessKeyId, secretAccessKey }, dbAccessConfig });
Step 3: Invoke the connector operations
Now, utilize the available connector operations.
redshiftdata:ExecutionResponse response = check redshiftdata->execute(`SELECT * FROM Users`); redshiftdata:DescriptionResponse descriptionResponse = check redshiftdata->describe(response.statementId); stream<User, redshiftdata:Error?> statementResult = check redshiftdata->getResultAsStream(response.statementId);
Step 4: Run the Ballerina application
Use the following command to compile and run the Ballerina program.
bal run
Examples
The aws.redshiftdata connector provides practical examples illustrating usage in various scenarios. Explore these examples.
-
Manage users - This example demonstrates how to use the Ballerina Redshift Data connector to perform SQL operations on an AWS Redshift cluster. It includes creating a table, inserting data, and querying data.
-
Music store - This example illustrates the process of creating an HTTP RESTful API with Ballerina to perform basic CRUD operations on a database, specifically AWS Redshift, involving setup, configuration, and running examples.