Module asb
Declarations
Definitions
ballerinax/asb Ballerina library
Overview
The Azure Service Bus is a fully managed enterprise message broker with message queues and publish-subscribe topics. It provides the capability to send and receive messages from Service Bus queues, topics, and subscriptions. The Azure Service Bus handles messages that include data representing any kind of information, including structured data encoded with common formats such as the following ones: JSON, XML, and Plain Text.
The Ballerina connector for Azure Service Bus allows you to connect to an Azure Service Bus via the Ballerina language.
This connector supports the following operations:
- Manage (Get/Create/Update/Delete/list) a queue, topic, subscription or rule.
- Send messages to a queue, topic, or subscription.
- Receive messages from a queue, topic, or subscription.
The Ballerina Azure Service Bus module utilizes Microsoft's Azure Service Bus JAVA SDK 7.13.1.
Setup guide
Before using this connector in your Ballerina application, complete the following:
Create a namespace in the Azure portal
To begin using Service Bus messaging in Azure, you must first create a namespace with a name that is unique across Azure. A namespace provides a scoping container for Service Bus resources within your application.
To create a namespace:
Step 1: Sign in to the Azure portal
If you don't have an Azure subscription, sign up for a free Azure account.
Step 2: Go to the Create Resource Service Bus menu
In the left navigation pane of the portal, select All services, select Integration from the list of categories, hover the mouse over Service Bus, and then select Create on the Service Bus tile.

Step 3: In the Basics tag of the Create namespace page, follow these steps:
-
For Subscription, choose an Azure subscription in which to create the namespace.
-
For Resource group, choose an existing resource group in which the namespace will live, or create a new one.
-
Enter a name for the namespace. The namespace name should adhere to the following naming conventions:
- The name must be unique across Azure. The system immediately checks to see if the name is available.
- The name length is at least 6 and at most 50 characters.
- The name can contain only letters, numbers, and hyphens “-“.
- The name must start with a letter and end with a letter or number.
- The name doesn't end with “-sb“ or “-mgmt“.
-
For Location, choose the region in which your namespace should be hosted.
-
For Pricing tier, select the pricing tier (Basic, Standard, or Premium) for the namespace. For this quickstart, select Standard.
Notice: If you want to use topics and subscriptions, choose either Standard or Premium. Topics/subscriptions aren't supported in the Basic pricing tier. If you selected the Premium pricing tier, specify the number of messaging units. The premium tier provides resource isolation at the CPU and memory level so that each workload runs in isolation. This resource container is called a messaging unit. A premium namespace has at least one messaging unit. You can select 1, 2, 4, 8, or 16 messaging units for each Service Bus Premium namespace. For more information, see Service Bus Premium Messaging.`
- Select Review + create at the bottom of the page.
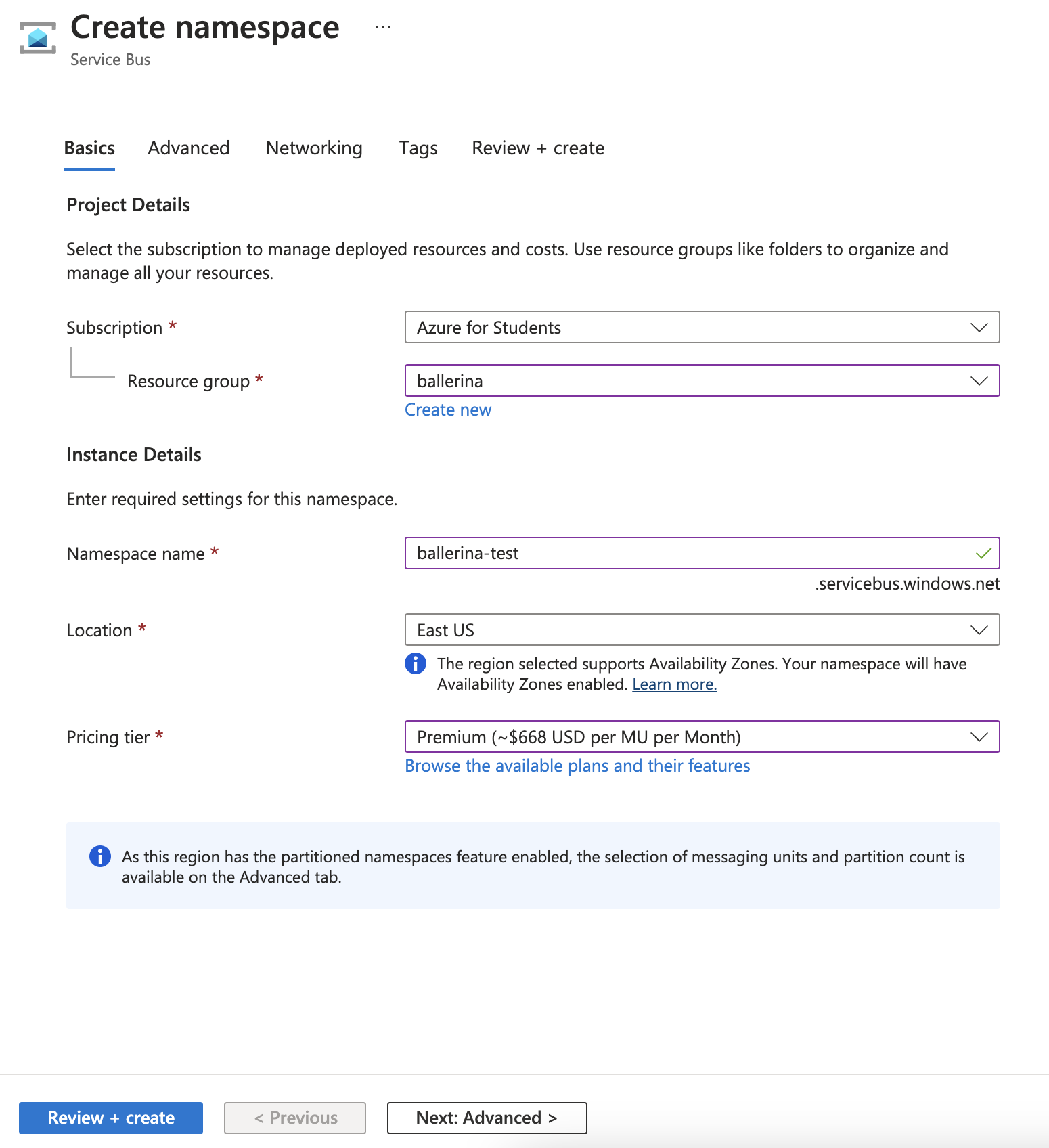
- On the Review + create page, review settings, and select Create.
Obtain tokens for authentication
To send and receive messages from a Service Bus queue or topic, clients must use a token that is signed by a shared access key, which is part of a shared access policy. A shared access policy defines a set of permissions that can be assigned to one or more Service Bus entities (queues, topics, event hubs, or relays). A shared access policy can be assigned to more than one entity, and a single entity can have more than one shared access policy assigned to it.
To obtain a token following steps should be followed:
-
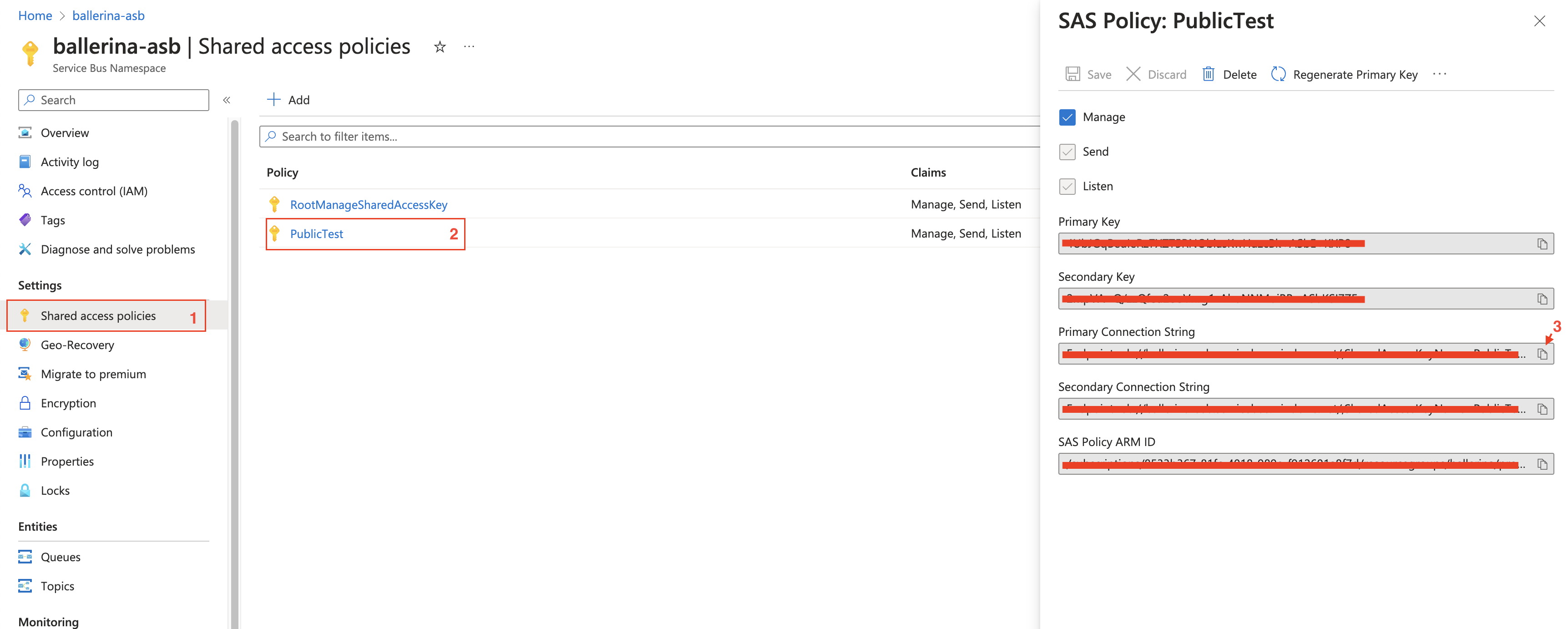
In the left navigation pane of the portal, select All services, select Integration from the list of categories, hover the mouse over Service Bus, and then select your namespace.
-
In the left navigation pane of the namespace page, select Shared access policies.
-
Click on the RootManageSharedAccessKey policy.
-
Copy the Primary Connection String value and save it in a secure location. This is the connection string that you use to authenticate with the Service Bus service.
Quickstart
To use the ASB connector in your Ballerina application, modify the .bal file as follows:
Step 1: Import connector
Import the ballerinax/asb module into the Ballerina project.
import ballerinax/asb;
Step 2: Create a new connector instance
Initialize an Admin Client
This can be done by providing a connection string.
configurable string connectionString = ?; asb:AdminClient admin = check new (connectionString);
Initialize a Message Sender client
This can be done by providing a connection string with a queue or topic name.
configurable string connectionString = ?; ASBServiceSenderConfig senderConfig = { connectionString: connectionString, entityType: QUEUE, topicOrQueueName: "myQueue" }; asb:MessageSender sender = check new (senderConfig);
Initialize a Message Receiver client
This can be done by providing a connection string with a queue name, topic name, or subscription path.
Here, the Receive mode is optional. (Default: PEEKLOCK)
configurable string connectionString = ?; ASBServiceReceiverConfig receiverConfig = { connectionString: connectionString, entityConfig: { queueName: "myQueue" }, receiveMode: PEEK_LOCK }; asb:MessageReceiver receiver = check new (receiverConfig);
Step 3: Invoke connector operation
Now you can use the remote operations available within the connector,
Create a queue in the Azure Service Bus
public function main() returns error? { asb:AdminClient admin = check new (adminConfig); check admin->createQueue("myQueue"); check admin->close(); }
Send a message to the Azure Service Bus
public function main() returns error? { asb:MessageSender queueSender = check new (senderConfig); string stringContent = "This is My Message Body"; byte[] byteContent = stringContent.toBytes(); int timeToLive = 60; // In seconds asb:ApplicationProperties applicationProperties = { properties: {a: "propertyValue1", b: "propertyValue2"} }; asb:Message message = { body: byteContent, contentType: asb:TEXT, timeToLive: timeToLive, applicationProperties: applicationProperties }; check queueSender->send(message); check queueSender->close(); }
Receive a message from the Azure Service Bus
public function main() returns error? { asb:MessageReceiver queueReceiver = check new (receiverConfig); int serverWaitTime = 60; // In seconds asb:Message|asb:Error? messageReceived = queueReceiver->receive(serverWaitTime); if (messageReceived is asb:Message) { log:printInfo("Reading Received Message : " + messageReceived.toString()); } else if (messageReceived is ()) { log:printError("No message in the queue."); } else { log:printError("Receiving message via Asb receiver connection failed."); } check queueReceiver->close(); }
Step 4: Run the Ballerina application
bal run
Examples
There are two sets of examples demonstrating the use of the Ballerina Azure Service Bus (ASB) Connector.
-
Management Related Examples: These examples cover operations related to managing the Service Bus, such as managing queues, topics, subscriptions, and rules.
-
Message Sending and Receiving Related Examples: This set includes examples for sending to and receiving messages from queues, topics, and subscriptions in the Service Bus.
Functions
getApplicationPropertyByName
Returns the application properties by its name
Parameters
- message Message - Represents a message that contains application properties
- name string - Represents the name of the application property that the user wants to retrieve.
Return Type
- anydata|error? - Returns null if the requested property does not exist
Clients
asb: Administrator
Ballerina Service Bus connector provides the capability to access Azure Service Bus SDK. Service Bus API provides data access to highly reliable queues and publish/subscribe topics of Azure Service Bus with deep feature capabilities.
Constructor
Initialize the Azure Service Bus Admin client. Create an Azure account and obtain tokens following this guide. Configure the connection string to have the required permission.
init (string connectionString)- connectionString string - Azure Service Bus connection string
createTopic
function createTopic(string topicName, *CreateTopicOptions topicOptions) returns TopicProperties|Error?Create a topic with the given name or name and options.
Parameters
- topicName string - Topic name
- topicOptions *CreateTopicOptions - Topic options to create the topic.This should be a record of type CreateTopicOptions
Return Type
- TopicProperties|Error? - Topic properties(Type of asb:TopicProperies) or error
getTopic
function getTopic(string topicName) returns TopicProperties|Error?Get the topic with the given name.
Parameters
- topicName string - Topic name
Return Type
- TopicProperties|Error? - Topic properties(Type of asb:TopicProperies) or error
updateTopic
function updateTopic(string topicName, *UpdateTopicOptions topicOptions) returns TopicProperties|Error?Update the topic with the given options.
Parameters
- topicName string - Topic name
- topicOptions *UpdateTopicOptions - Topic options to update the topic.This should be a record of type UpdateTopicOptions
Return Type
- TopicProperties|Error? - Topic properties(Type of asb:TopicProperies) or error
listTopics
List the topics.
deleteTopic
Delete the topic with the given name.
Parameters
- topicName string - Topic name
Return Type
- Error? - Error or nil
createSubscription
function createSubscription(string topicName, string subscriptionName, *CreateSubscriptionOptions subscriptionOptions) returns SubscriptionProperties|Error?Create a subscription with the given name or name and options.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
- subscriptionName string - Name of the subscription
- subscriptionOptions *CreateSubscriptionOptions - Subscription options to create the subscription.This should be a record of type CreateSubscriptionOptions.
Return Type
- SubscriptionProperties|Error? - Subscription properties(Type of asb:SubscriptionProperies) or error
getSubscription
function getSubscription(string topicName, string subscriptionName) returns SubscriptionProperties|Error?Get the subscription with the given name.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
- subscriptionName string - Name of the subscription
Return Type
- SubscriptionProperties|Error? - Subscription properties(Type of asb:SubscriptionProperies) or error
updateSubscription
function updateSubscription(string topicName, string subscriptionName, *UpdateSubscriptionOptions subscriptionOptions) returns SubscriptionProperties|Error?Update the subscription with the given options.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
- subscriptionName string - Name of the subscription
- subscriptionOptions *UpdateSubscriptionOptions - Subscription options to update the subscription.This should be a record of type UpdateSubscriptionOptions
Return Type
- SubscriptionProperties|Error? - Subscription properties(Type of asb:SubscriptionProperies) or error
listSubscriptions
function listSubscriptions(string topicName) returns SubscriptionList|Error?List the subscriptions.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
Return Type
- SubscriptionList|Error? - Subscription list(Type of asb:SubscriptionList) or error
deleteSubscription
Delete the subscription with the given name.
Return Type
- Error? - Error or nil
topicExists
Get the status of existance of a topic with the given name.
Parameters
- topicName string - Topic name
subscriptionExists
Get the status of existance of a subscription with the given name.
createRule
function createRule(string topicName, string subscriptionName, string ruleName, *CreateRuleOptions ruleOptions) returns RuleProperties|Error?Create a rule with the given name or name and options.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
- subscriptionName string - Name of the subscription
- ruleName string - Name of the rule
- ruleOptions *CreateRuleOptions - Rule options to create the rule.This should be a record of type CreateRuleOptions
Return Type
- RuleProperties|Error? - Rule properties(Type of asb:RuleProperies) or error
getRule
function getRule(string topicName, string subscriptionName, string ruleName) returns RuleProperties|Error?Delete the rule with the given name.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
- subscriptionName string - Name of the subscription associated with rule
- ruleName string - Rule name
Return Type
- RuleProperties|Error? - Error or nil
updateRule
function updateRule(string topicName, string subscriptionName, string ruleName, *UpdateRuleOptions ruleOptions) returns RuleProperties|Error?Update the rule with the options.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
- subscriptionName string - Name of the subscription associated with rule
- ruleName string - Rule name
- ruleOptions *UpdateRuleOptions - Rule options to update the rule.This should be a record of type UpdateRuleOptions
Return Type
- RuleProperties|Error? - Rule properties(Type of asb:RuleProperies) or error
listRules
List the rules.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
- subscriptionName string - Name of the subscription
deleteRule
Delete the rule with the given name.
Parameters
- topicName string - Name of the topic associated with subscription
- subscriptionName string - Name of the subscription associated with rule
- ruleName string - Rule name
Return Type
- Error? - Error or nil
createQueue
function createQueue(string queueName, *CreateQueueOptions queueOptions) returns QueueProperties|Error?Create a queue with the given name or name and options.
Parameters
- queueName string - Name of the queue
- queueOptions *CreateQueueOptions - Queue options to create the queue.This should be a record of type CreateQueueOptions
Return Type
- QueueProperties|Error? - Queue properties(Type of asb:QueueProperties) or error
getQueue
function getQueue(string queueName) returns QueueProperties|Error?Get the queue with the given name.
Parameters
- queueName string - Name of the queue
Return Type
- QueueProperties|Error? - Queue properties(Type of asb:QueueProperties) or error
updateQueue
function updateQueue(string queueName, *UpdateQueueOptions queueOptions) returns QueueProperties|Error?Update the queue with the options.Q
Parameters
- queueName string - Name of the queue
- queueOptions *UpdateQueueOptions - Queue options to update the queue.This should be a record of type UpdateQueueOptions
Return Type
- QueueProperties|Error? - Queue properties(Type of asb:QueueProperties) or error
listQueues
List the queues.
deleteQueue
Delete the queue with the given name.
Parameters
- queueName string - Name of the queue
Return Type
- Error? - Error or nil
queueExists
Check whether the queue exists.
Parameters
- queueName string - Name of the queue
asb: Caller
Represents a ASB caller, which can be used to mark messages as complete, abandon, deadLetter, or defer.
complete
function complete() returns Error?Complete message from queue or subscription based on messageLockToken. Declares the message processing to be successfully completed, removing the message from the queue.
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to complete message or else()
abandon
function abandon(* propertiesToModify) returns Error?Abandon message from queue or subscription based on messageLockToken. Abandon processing of the message for the time being, returning the message immediately back to the queue to be picked up by another (or the same) receiver.
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to abandon message or else()
deadLetter
function deadLetter(*DeadLetterOptions options) returns Error?Dead-Letter the message & moves the message to the Dead-Letter Queue based on messageLockToken. Transfer the message from the primary queue into a special "dead-letter sub-queue".
Parameters
- options *DeadLetterOptions - Options to specify while putting message in dead-letter queue
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to deadletter message or else()
defer
function defer(* propertiesToModify) returns Error?Defer the message in a Queue or Subscription based on messageLockToken. It prevents the message from being directly received from the queue by setting it aside such that it must be received by sequence number.
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to defer message or else sequence number
asb: MessageReceiver
Ballerina Service Bus connector provides the capability to access Azure Service Bus SDK. Service Bus API provides data access to highly reliable queues and publish/subscribe topics of Azure Service Bus with deep feature capabilities.
Constructor
Initializes the connector. During initialization you can pass the Shared Access Signature (SAS) authentication credentials Create an Azure account and obtain tokens following this guide. Configure the connection string to have the required permission.
init (ASBServiceReceiverConfig config)- config ASBServiceReceiverConfig - Azure service bus receiver configuration.(Default receiver mode is PEEK_LOCK)
receive
Receive message from queue or subscription.
Parameters
- serverWaitTime int? (default 60) - Specified server wait time in seconds to receive message (optional)
- T typedesc<Message> (default <>) - Expected type of the message. This can be either a
asb:Messageor a subtype of it.
- deadLettered boolean (default false) - If set to
true, messages from dead-letter queue will be received. (optional)
Return Type
- T|Error? - A
asb:Messagerecord if message is received,()if no message is in the queue or else anasb:Errorif failed to receive message
receivePayload
function receivePayload(int? serverWaitTime, typedesc<anydata> T, boolean deadLettered) returns T|ErrorReceive message payload from queue or subscription.
Parameters
- serverWaitTime int? (default 60) - Specified server wait time in seconds to receive message (optional)
- T typedesc<anydata> (default <>) - Expected type of the message. This can be any subtype of
anydatatype
- deadLettered boolean (default false) - If set to
true, messages from dead-letter queue will be received. (optional)
Return Type
- T|Error - A
asb:Messagerecord if message is received,()if no message is in the queue or else anasb:Errorif failed to receive message
receiveBatch
function receiveBatch(int maxMessageCount, int? serverWaitTime, boolean deadLettered) returns MessageBatch|Error?Receive batch of messages from queue or subscription.
Parameters
- maxMessageCount int - Maximum message count to receive in a batch
- serverWaitTime int? (default ()) - Specified server wait time in seconds to receive message (optional)
- deadLettered boolean (default false) - If set to
true, messages from dead-letter queue will be received. (optional)
Return Type
- MessageBatch|Error? - A
asb:MessageBatchrecord if batch is received,()if no batch is in the queue or else anasb:Errorif failed to receive batch
complete
Complete message from queue or subscription based on messageLockToken. Declares the message processing to be successfully completed, removing the message from the queue.
Parameters
- message Message -
asb:Messagerecord
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to complete message or else()
abandon
Abandon message from queue or subscription based on messageLockToken. Abandon processing of the message for the time being, returning the message immediately back to the queue to be picked up by another (or the same) receiver.
Parameters
- message Message -
asb:Messagerecord
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to abandon message or else()
deadLetter
function deadLetter(Message message, string deadLetterReason, string? deadLetterErrorDescription) returns Error?Dead-Letter the message & moves the message to the Dead-Letter Queue based on messageLockToken. Transfer the message from the primary queue into a special "dead-letter sub-queue".
Parameters
- message Message -
asb:Messagerecord
- deadLetterReason string (default "DEADLETTERED_BY_RECEIVER") - The deadletter reason (optional)
- deadLetterErrorDescription string? (default ()) - The deadletter error description (optional)
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to deadletter message or else()
defer
Defer the message in a Queue or Subscription based on messageLockToken. It prevents the message from being directly received from the queue by setting it aside such that it must be received by sequence number.
Parameters
- message Message -
asb:Messagerecord
receiveDeferred
Receives a deferred Message. Deferred messages can only be received by using sequence number and return Message object.
Parameters
- sequenceNumber int - Unique number assigned to a message by Service Bus. The sequence number is a unique 64-bit integer assigned to a message as it is accepted and stored by the broker and functions as its true identifier.
Return Type
renewLock
The operation renews lock on a message in a queue or subscription based on messageLockToken.
Parameters
- message Message -
asb:Messagerecord
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to renew message or else()
close
function close() returns Error?Closes the ASB sender connection.
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to close connection or else()
asb: MessageSender
Ballerina Service Bus connector provides the capability to access Azure Service Bus SDK. Service Bus API provides data access to highly reliable queues and publish/subscribe topics of Azure Service Bus with deep feature capabilities.
Constructor
Initializes the connector. During initialization you can pass the Shared Access Signature (SAS) authentication credentials Create an Azure account and obtain tokens following this guide. Configure the connection string to have the required permission.
init (ASBServiceSenderConfig config)- config ASBServiceSenderConfig - Azure service bus sender configuration
send
Send message to queue or topic with a message body.
Parameters
- message Message - Azure service bus message representation (
asb:Messagerecord)
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to send message or else()
sendPayload
function sendPayload(anydata messagePayload) returns Error?Send message to queue or topic with a message body.
Parameters
- messagePayload anydata - Message body
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to send message or else()
schedule
Sends a scheduled message to the Azure Service Bus entity this sender is connected to. A scheduled message is enqueued and made available to receivers only at the scheduled enqueue time.
Parameters
- message Message - Message to be scheduled
- scheduledEnqueueTime Civil - Datetime at which the message should appear in the Service Bus queue or topic
Return Type
cancel
Cancels the enqueuing of a scheduled message, if they are not already enqueued.
Parameters
- sequenceNumber int - The sequence number of the message to cancel
Return Type
- Error? - If the message could not be cancelled
sendBatch
function sendBatch(MessageBatch messageBatch) returns Error?Send batch of messages to queue or topic.
Parameters
- messageBatch MessageBatch - Azure service bus batch message representation (
asb:MessageBatchrecord)
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to send message or else()
close
function close() returns Error?Closes the ASB sender connection.
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif failed to close connection or else()
Service types
asb: Service
The ASB service type.
Constants
asb: BYTE_ARRAY
asb: DEFAULT_MAX_MESSAGE_COUNT
asb: DEFAULT_MESSAGE_LOCK_TOKEN
asb: DEFAULT_SERVER_WAIT_TIME
asb: DEFAULT_TIME_TO_LIVE
asb: JSON
asb: TEXT
asb: XML
Enums
asb: AccessRight
Access rights
Members
asb: AmqpRetryMode
The type of approach to apply when calculating the delay between retry attempts.
Members
asb: EntityStatus
Entity status
Members
asb: EntityType
Message entity types
Members
asb: LogLevel
Log levels
Members
asb: ReceiveMode
Message receiver modes
Members
Listeners
asb: Listener
Represents a ASB consumer listener.
Constructor
Creates a new asb:Listener.
listener asb:Listener asbListener = check new (
connectionString = "xxxxxxxx",
entityConfig = {
queueName: "test-queue"
},
autoComplete = false
);
init (*ListenerConfiguration config)- config *ListenerConfiguration - ASB listener configurations
attach
Attaches an asb:Service to a listener.
check asbListener.attach(asbService);
Parameters
- 'service Service - The service instance
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif there is an error or else()
detach
Detaches an asb:Service from the the listener.
check asbListener.detach(asbService);
Parameters
- 'service Service - The service to be detached
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif there is an error or else()
'start
function 'start() returns Error?Starts the asb:Listener.
check asbListener.'start();
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif there is an error or else()
gracefulStop
function gracefulStop() returns Error?Stops the asb:Listener gracefully.
check asbListener.gracefulStop();
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif there is an error or else()
immediateStop
function immediateStop() returns Error?Stops the asb:Listener immediately.
check asbListener.immediateStop();
Return Type
- Error? - An
asb:Errorif there is an error or else()
Records
asb: AmqpRetryOptions
Set of options that can be specified to influence how the retry attempts are made.
Fields
- maxRetries int(default 3) - Maximum number of retry attempts
- delay decimal(default 10) - Delay between retry attempts in seconds
- maxDelay decimal(default 60) - Maximum permissible delay between retry attempts in seconds
- tryTimeout decimal(default 60) - Maximum duration to wait for completion of a single attempt in seconds
- retryMode AmqpRetryMode(default FIXED) - Approach to use for calculating retry delays
asb: ApplicationProperties
Azure service bus message, application specific properties representation.
Fields
- properties map<anydata>? - Key-value pairs for each brokered property (optional)
asb: ASBServiceReceiverConfig
Configurations used to create an asb:Connection.
Fields
- connectionString string - Service bus connection string with Shared Access Signatures
ConnectionString format: Endpoint=sb://namespace_DNS_Name;EntityPath=EVENT_HUB_NAME; SharedAccessKeyName=SHARED_ACCESS_KEY_NAME;SharedAccessKey=SHARED_ACCESS_KEY or Endpoint=sb://namespace_DNS_Name;EntityPath=EVENT_HUB_NAME; SharedAccessSignatureToken=SHARED_ACCESS_SIGNATURE_TOKEN
- entityConfig TopicSubsConfig|QueueConfig - This field holds the configuration details of either a topic or a queue. The type of the entity is determined by the entityType field. The actual configuration details are stored in either a TopicSubsConfig or a QueueConfig record
- receiveMode ReceiveMode(default PEEK_LOCK) - This field holds the receive modes(RECEIVE_AND_DELETE/PEEK_LOCK) for the connection. The receive mode determines how messages are retrieved from the entity. The default value is PEEK_LOCK
- maxAutoLockRenewDuration int(default 300) - Max lock renewal duration under PEEK_LOCK mode in seconds. Setting to 0 disables auto-renewal. For RECEIVE_AND_DELETE mode, auto-renewal is disabled. Default 300 seconds.
- amqpRetryOptions AmqpRetryOptions(default {}) - Retry configurations related to underlying AMQP message receiver
asb: ASBServiceSenderConfig
Holds the configuration details needed to create a sender connection to Azure Service Bus.
Fields
- entityType EntityType - An enumeration value of type EntityType, which specifies whether the connection is for a topic or a queue. The valid values are TOPIC and QUEUE
- topicOrQueueName string - A string field that holds the name of the topic or queue
- connectionString string - A string field that holds the Service Bus connection string with Shared Access Signatures.
- amqpRetryOptions AmqpRetryOptions(default {}) - Retry configurations related to underlying AMQP message sender
asb: AuthorizationRule
AuthorizationRule.
Fields
- accessRights AccessRight[] - The rights associated with the rule
- claimType string - The type of the claim
- claimValue string - The value of the claim
- createdAt string - The exact time the rule was created
- keyName string - The name of the key that was used
- modifiedAt string - The exact time the rule was modified
- primaryKey string - The primary key associated with the rule
- secondaryKey string - The secondary key associated with the rule
asb: CreateQueueOptions
Create Queue Options.
Fields
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the queue is automatically deleted. The minimum duration is 5 minutes.
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration? - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value. This is the duration after which the message expires, starting from when the message is sent to Service Bus.
- duplicateDetectionHistoryTimeWindow Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes.
- forwardDeadLetteredMessagesTo string? - The name of the recipient entity to which all the dead-lettered messages of this subscription are forwarded to.
- forwardTo string? - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the queue are forwarded to
- lockDuration Duration? - ISO 8601 timespan duration of a peek-lock; that is, the amount of time that the message is locked for other receivers. The maximum value for LockDuration is 5 minutes; the default value is 1 minute.
- maxDeliveryCount int? - The maximum delivery count. A message is automatically deadlettered after this number of deliveries. Default value is 10.
- maxMessageSizeInKilobytes int? - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- maxSizeInMegabytes int? - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- status EntityStatus? - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- userMetadata string? - Metadata associated with the queue
- enableBatchedOperations boolean? - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- deadLetteringOnMessageExpiration boolean? - Value that indicates whether this queue has dead letter support when a message expires
- requiresDuplicateDetection boolean? - Value indicating if this queue requires duplicate detection
- enablePartitioning boolean? - Value that indicates whether the queue is to be partitioned across multiple message brokers
- requiresSession boolean? - Value that indicates whether the queue supports the concept of sessions
asb: CreateRuleOptions
Create Rule Options.
Fields
- rule SqlRule? - Represents a SQL filter which is a composition of an expression and an action that is executed in the pub/sub pipeline
asb: CreateSubscriptionOptions
Create Subscription Options.
Fields
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the subscription is automatically deleted
- enableBatchedOperations boolean? - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- deadLetteringOnMessageExpiration boolean? - Value that indicates whether this subscription has dead letter support when a message expires
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration? - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value
- deadLetteringOnFilterEvaluationExceptions boolean? - Value that indicates whether this subscription has dead letter support when a message expires
- forwardDeadLetteredMessagesTo string? - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the subscription are forwarded to
- forwardTo string? - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the subscription are forwarded to
- lockDuration Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes
- maxDeliveryCount int? - The maximum delivery count. A message is automatically deadlettered after this number of deliveries. Default value is 10
- requiresSession boolean? - A value that indicates whether the queue supports the concept of sessions
- status EntityStatus? - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- userMetadata string? - Metadata associated with the subscription
asb: CreateTopicOptions
Create Topic Options.
Fields
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the queue is automatically deleted. The minimum duration is 5 minutes
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration? - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value. This is the duration after which the message expires, starting from when the message is sent to Service Bus.
- duplicateDetectionHistoryTimeWindow Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes.
- lockDuration Duration? - ISO 8601 timespan duration of a peek-lock; that is, the amount of time that the message is locked for other receivers. The maximum value for LockDuration is 5 minutes; the default value is 1 minute.
- maxDeliveryCount int? - The maximum delivery count. A message is automatically deadlettered after this number of deliveries. Default value is 10.
- maxMessageSizeInKilobytes int? - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- maxSizeInMegabytes int? - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- status EntityStatus? - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- userMetadata string? - Metadata associated with the queue
- enableBatchedOperations boolean? - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- deadLetteringOnMessageExpiration boolean? - Value that indicates whether this queue has dead letter support when a message expires
- requiresDuplicateDetection boolean? - Value indicating if this queue requires duplicate detection
- enablePartitioning boolean? - Value that indicates whether the queue is to be partitioned across multiple message brokers
- requiresSession boolean? - Value that indicates whether the queue supports the concept of sessions
- supportOrdering boolean? - Defines whether ordering needs to be maintained
asb: CustomConfiguration
Represents Custom configurations for the ASB connector.
Fields
- logLevel LogLevel(default OFF) - Enables the connector debug log prints (log4j log levels), default: OFF
asb: DeadLetterOptions
Options to specify when sending an asb:Message received via asb:ReceiveMode#PEEK_LOCK to the dead-letter queue.
Fields
- deadLetterReason string? - The deadletter reason
- deadLetterErrorDescription string? - The deadletter error description
- propertiesToModify map<anydata>? - Message properties to modify
asb: Duration
Duration.
Fields
- seconds int(default 0) - Seconds
- nanoseconds int(default 0) - Nanoseconds
asb: ErrorContext
Represents message retrieval error context.
Fields
- entityPath string - The entity path of the error source
- className string - The name of the originating class
- namespace string - The namespace of the error source
- errorSource string - The error source, such as a function or action name
- reason string - The reason for the error
asb: ListenerConfiguration
Represents Azure service bus listener configuration.
Fields
- Fields Included from *ASBServiceReceiverConfig
- connectionString string
- entityConfig TopicSubsConfig|QueueConfig
- receiveMode ReceiveMode
- maxAutoLockRenewDuration int
- amqpRetryOptions AmqpRetryOptions
- anydata...
- autoComplete boolean(default true) - Enables auto-complete and auto-abandon of received messages
- prefetchCount int(default 0) - The number of messages to prefetch
- maxConcurrency int(default 1) - Max concurrent messages that this listener should process
asb: Message
Azure service bus Message representation.
Fields
- body anydata - Message body, Here the connector supports AMQP message body types - DATA and VALUE, However, DATA type message bodies
will be received in Ballerina Byte[] type. VALUE message bodies can be any primitive AMQP type. therefore, the connector
supports for string, int or byte[]. Please refer Azure docs (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/java/api/com.azure.core.amqp.models.amqpmessagebody?view=azure-java-stable)
and AMQP docs (https://qpid.apache.org/amqp/type-reference.html#PrimitiveTypes)
- contentType string(default BYTE_ARRAY) - Message content type, with a descriptor following the format of
RFC2045, (e.g.application/json) (optional)
- messageId string? - Message Id (optional)
- to string? - Message to (optional)
- replyTo string? - Message reply to (optional)
- replyToSessionId string? - Identifier of the session to reply to (optional)
- label string? - Message label (optional)
- sessionId string? - Message session Id (optional)
- correlationId string? - Message correlationId (optional)
- partitionKey string? - Message partition key (optional)
- timeToLive int? - Message time to live in seconds (optional)
- sequenceNumberreadonly int? - Message sequence number (optional)
- lockTokenreadonly string? - Message lock token (optional)
- applicationProperties ApplicationProperties? - Message broker application specific properties (optional)
- deliveryCount int? - Number of times a message has been delivered in a queue/subscription
- enqueuedTime string? - Timestamp indicating when a message was added to the queue/subscription
- enqueuedSequenceNumber int? - Sequence number assigned to a message when it is added to the queue/subscription
- deadLetterErrorDescription string? - Error description of why a message went to a dead-letter queue
- deadLetterReason string? - Reason why a message was moved to a dead-letter queue
- deadLetterSource string? - Original queue/subscription where the message was before being moved to the dead-letter queue
- state string? - Current state of a message in the queue/subscription, could be "Active", "Scheduled", "Deferred", etc.
asb: MessageBatch
Azure service bus message batch representation.
Fields
- messageCount int(default -1) - Number of messages in a batch
- messages Message[](default []) - Array of Azure service bus message representation (Array of Message records)
asb: Options
Represents Custom configurations for the ASB connector
Fields
- logLevel LogLevel(default OFF) - Enables the connector debug log prints (log4j log levels), default: OFF
asb: QueueConfig
This record holds the configuration details of a queue in Azure Service Bus.
Fields
- queueName string - A string field that holds the name of the queue
asb: QueueList
Queue List.
Fields
- list QueueProperties[] - The list of queues
asb: QueueProperties
QueueProperties.
Fields
- authorizationRules AuthorizationRule[] - Authorization rules for resource
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the queue is automatically deleted. The minimum duration is 5 minutes.
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value. This is the duration after which the message expires, starting from when the message is sent to Service Bus.
- duplicateDetectionHistoryTimeWindow Duration - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes.
- forwardDeadLetteredMessagesTo string - The name of the recipient entity to which all the dead-lettered messages of this subscription are forwarded to.
- forwardTo string - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the queue are forwarded to.
- lockDuration Duration - ISO 8601 timespan duration of a peek-lock; that is, the amount of time that the message is locked for other receivers. The maximum value for LockDuration is 5 minutes; the default value is 1 minute.
- maxDeliveryCount int - The maximum delivery count. A message is automatically deadlettered after this number of deliveries. Default value is 10.
- maxMessageSizeInKilobytes int - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- maxSizeInMegabytes int - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- name string - The name of the queue to create
- status EntityStatus - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- userMetadata string - Metadata associated with the queue
- enableBatchedOperations boolean - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- deadLetteringOnMessageExpiration boolean - Value that indicates whether this queue has dead letter support when a message expires
- requiresDuplicateDetection boolean - Value indicating if this queue requires duplicate detection
- enablePartitioning boolean - Value that indicates whether the queue is to be partitioned across multiple message brokers
- requiresSession boolean - Value that indicates whether the queue supports the concept of sessions
asb: RuleList
Rule List.
Fields
- list RuleProperties[] - The list of rules
asb: RuleProperties
Rule Properties.
Fields
- rule SqlRule - Represents a SQL filter which is a composition of an expression and an action that is executed in the pub/sub pipeline
- name string - The name of the rule
asb: SqlRule
SQL Rule.
Fields
- filter string - Represents a filter which is a composition of an expression and an action that is executed in the pub/sub pipeline
- action string - Represents set of actions written in Sql language-based syntax
asb: SubscriptionList
Subscription List.
Fields
- list SubscriptionProperties[] - The list of subscriptions
asb: SubscriptionProperties
SubscriptionProperties.
Fields
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the subscription is automatically deleted
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value
- forwardDeadLetteredMessagesTo string - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the subscription are forwarded to
- forwardTo string - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the subscription are forwarded to
- lockDuration Duration - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes
- maxDeliveryCount int - The maximum delivery count. A message is automatically deadlettered after this number of deliveries. Default value is 10
- status EntityStatus - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- subscriptionName string - The name of the subscription
- topicName string - The name of the topic under which subscription exists
- userMetadata string - Metadata associated with the subscription
- enableBatchedOperations boolean - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- deadLetteringOnFilterEvaluationExceptions boolean - A value that indicates whether this subscription has dead letter support when a message expires
- deadLetteringOnMessageExpiration boolean - A value that indicates whether this subscription has dead letter support when a message expires
- requiresSession boolean - A value that indicates whether the queue supports the concept of sessions
asb: TopicList
Topic List
Fields
- list TopicProperties[] - The list of topics.
asb: TopicProperties
TopicProperties.
Fields
- name string - The name of the topic to create
- authorizationRules AuthorizationRule[] - Authorization rules for resource
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the queue is automatically deleted. The minimum duration is 5 minutes
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value. This is the duration after which the message expires, starting from when the message is sent to Service Bus.
- duplicateDetectionHistoryTimeWindow Duration - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes.
- maxMessageSizeInKilobytes int - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue.
- maxSizeInMegabytes int - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue.
- status EntityStatus - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- userMetadata string - Metadata associated with the queue
- enableBatchedOperations boolean - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- requiresDuplicateDetection boolean - Value indicating if this queue requires duplicate detection
- enablePartitioning boolean - Value that indicates whether the queue is to be partitioned across multiple message brokers
- supportOrdering boolean - Defines whether ordering needs to be maintained
asb: TopicSubsConfig
This record holds the configuration details of a topic and its associated subscription in Azure Service Bus.
Fields
- topicName string - A string field that holds the name of the topic
- subscriptionName string - A string field that holds the name of the subscription associated with the topic
asb: UpdateQueueOptions
Update Queue Options.
Fields
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the queue is automatically deleted. The minimum duration is 5 minutes.
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration? - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value. This is the duration after which the message expires, starting from when the message is sent to Service Bus.
- duplicateDetectionHistoryTimeWindow Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes.
- forwardDeadLetteredMessagesTo string? - The name of the recipient entity to which all the dead-lettered messages of this subscription are forwarded to.
- forwardTo string? - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the queue are forwarded to
- lockDuration Duration? - ISO 8601 timespan duration of a peek-lock; that is, the amount of time that the message is locked for other receivers. The maximum value for LockDuration is 5 minutes; the default value is 1 minute.
- maxDeliveryCount int? - The maximum delivery count. A message is automatically deadlettered after this number of deliveries. Default value is 10.
- maxMessageSizeInKilobytes int? - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- maxSizeInMegabytes int? - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- status EntityStatus? - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- userMetadata string? - Metadata associated with the queue
- enableBatchedOperations boolean? - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- deadLetteringOnMessageExpiration boolean? - Value that indicates whether this queue has dead letter support when a message expires
- requiresDuplicateDetection boolean? - Value indicating if this queue requires duplicate detection
- enablePartitioning boolean? - Value that indicates whether the queue is to be partitioned across multiple message brokers
- requiresSession boolean? - Value that indicates whether the queue supports the concept of sessions
asb: UpdateRuleOptions
Update Rule Options.
Fields
- rule SqlRule? - Represents a SQL filter which is a composition of an expression and an action that is executed in the pub/sub pipeline
asb: UpdateSubscriptionOptions
Update Subscription Options.
Fields
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the subscription is automatically deleted
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration? - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value
- deadLetteringOnMessageExpiration boolean? - Value that indicates whether this subscription has dead letter support when a message expires
- deadLetteringOnFilterEvaluationExceptions boolean? - Value that indicates whether this subscription has dead letter support when a message expires
- enableBatchedOperations boolean? - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- forwardDeadLetteredMessagesTo string? - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the subscription are forwarded to
- forwardTo string? - The name of the recipient entity to which all the messages sent to the subscription are forwarded to
- lockDuration Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes
- maxDeliveryCount int? - The maximum delivery count. A message is automatically deadlettered after this number of deliveries. Default value is 10
- status EntityStatus? - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- userMetadata string? - Metadata associated with the subscription
asb: UpdateTopicOptions
Upadate Topic Propertise.
Fields
- autoDeleteOnIdle Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan idle interval after which the queue is automatically deleted. The minimum duration is 5 minutes.
- defaultMessageTimeToLive Duration? - ISO 8601 default message timespan to live value. This is the duration after which the message expires, starting from when the message is sent to Service Bus.
- duplicateDetectionHistoryTimeWindow Duration? - ISO 8601 timeSpan structure that defines the duration of the duplicate detection history. The default value is 10 minutes.
- maxDeliveryCount int? - The maximum delivery count. A message is automatically deadlettered after this number of deliveries. Default value is 10.
- maxMessageSizeInKilobytes int? - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- maxSizeInMegabytes int? - The maximum size of the queue in megabytes, which is the size of memory allocated for the queue
- status EntityStatus? - Enumerates the possible values for the status of a messaging entity
- userMetadata string? - Metadata associated with the queue
- enableBatchedOperations boolean? - Value that indicates whether server-side batched operations are enabled
- deadLetteringOnMessageExpiration boolean? - Value that indicates whether this queue has dead letter support when a message expires
- requiresDuplicateDetection boolean? - Value indicating if this queue requires duplicate detection
- enablePartitioning boolean? - Value that indicates whether the queue is to be partitioned across multiple message brokers
- requiresSession boolean? - Value that indicates whether the queue supports the concept of sessions
- supportOrdering boolean? - Defines whether ordering needs to be maintained
Errors
asb: Error
Defines the common error type for the module.
Intersection types
asb: MessageRetrievalError
MessageRetrievalError
Error type to capture the errors occurred while retrieving messages in Azure service bus listener.
Import
import ballerinax/asb;Metadata
Released date: over 1 year ago
Version: 3.8.0
License: Apache-2.0
Compatibility
Platform: java17
Ballerina version: 2201.8.0
GraalVM compatible: Yes
Pull count
Total: 4623
Current verison: 73
Weekly downloads
Keywords
IT Operations/Message Brokers
Cost/Paid
Vendor/Microsoft
Contributors
Dependencies